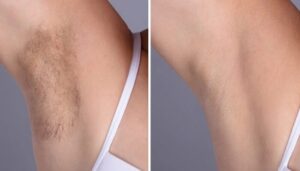
Laser hair removal in Dubai, when performed by experienced specialists, is a safe and effective way to achieve smooth, hair-free skin. Among the Best Doctors in Dubai, Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai stands out, offering state-of-the-art treatments under the care of Celebrity Doctor in Dubai, Dr. Perfect. Using advanced technology, Laser Hair Removal in Dubai at this clinic ensures long-lasting, almost painless results for both males and females.
Trusted Experts: Best Doctors in Dubai for Laser Hair Removal
Why Choose the Best Doctors in Dubai?
Best Doctors in Dubai combine medical expertise with cosmetic precision. At Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai, every patient receives a tailored approach to Permanent Hair Removal in Dubai, ensuring safety and comfort.
Meet Dr. Perfect, Celebrity Doctor in Dubai
Dr. Perfect is recognized as a Celebrity Doctor in Dubai, trusted by clients for his professional care and exceptional results in Laser Hair Removal Dubai. The clinic’s focus on patient safety makes it one of the Best Doctors in Dubai for hair removal.
Specialized Laser Hair Removal Doctors in Dubai
The Laser hair removal Doctors in dubai at Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai offer treatments designed for both males and females. Each session is personalized to the patient’s skin type, hair color, and hair thickness, guaranteeing optimal results in Laser Hair Removal in Dubai.
Advanced Technology for Permanent Hair Removal
Using FDA-approved equipment, Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai delivers Permanent Hair Removal in Dubai safely and efficiently. Patients experience minimal discomfort while achieving smooth, hair-free skin.
Celebrity Clinic in Dubai: Experience Luxury and Precision
Why a Celebrity Clinic in Dubai Matters
A Celebrity Clinic in Dubai, like Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai, offers not only expertise but also a luxurious environment for patients. Treatments here combine medical excellence with comfort, ensuring a superior Laser Hair Removal Dubai experience.
Celebrity Doctor in Dubai – Dr. Perfect
Dr. Perfect, a renowned Celebrity Doctor in Dubai, leads the team of Laser Hair Removal Doctors in Dubai, providing treatments that are both safe and effective. The clinic is popular among high-profile clients seeking Best Laser Hair Removal in Dubai.
Laser Hair Removal in Dubai: Procedure and Benefits
Safe and Effective Treatments
At Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai, Laser Hair Removal in Dubai uses cutting-edge lasers for precise, pain-minimized sessions. The procedure is suitable for all skin types and offers Permanent Hair Removal in Dubai with long-lasting results.
Average Cost and Accessibility
For male and female patients, the average cost of Laser Hair Removal in Dubai Jumeirah starts at AED 299 (excluding VAT). At Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai, affordable pricing does not compromise on quality or safety.
Target Areas for Laser Hair Removal
The clinic provides treatment for multiple areas, including face, arms, legs, underarms, and more. The Best Laser Hair Removal in Dubai at Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai ensures smooth skin across all treated regions.
Why Choose Perfect Doctors Clinic for Laser Hair Removal Dubai?
-
Advanced Technology – FDA-approved lasers ensure effective Laser Hair Removal in Dubai.
-
Expert Doctors – Recognized Laser Hair Removal Doctors in Dubai provide personalized care.
-
Celebrity-Level Service – As a Celebrity Clinic in Dubai, the clinic maintains high standards.
-
Permanent Results – Achieve Permanent Hair Removal in Dubai safely and effectively.
FAQs About Laser Hair Removal in Dubai
Q1: Who are the Best Doctors in Dubai for Laser Hair Removal?
Best Doctors in Dubai for hair removal include Dr. Perfect at Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai, known for safe, advanced treatments.
Q2: Is Laser Hair Removal at Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai safe for all skin types?
Yes, Laser Hair Removal in Dubai at Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai is safe for both male and female patients, including sensitive skin areas.
Q3: What is the average cost of Laser Hair Removal in Dubai Jumeirah?
The average cost of Laser Hair Removal in Dubai Jumeirah starts at AED 299 (excluding VAT). The clinic offers flexible options for multiple treatment sessions.
Q4: Can Laser Hair Removal be permanent?
Yes, with advanced technology at Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai, you can achieve Permanent Hair Removal in Dubai safely and effectively.
Q5: Are treatments at a Celebrity Clinic in Dubai more effective?
Celebrity Clinic in Dubai, like Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai, combines expert care, advanced technology, and personalized attention to ensure the Best Laser Hair Removal in Dubai results.
Conclusion
For anyone seeking Best Doctors in Dubai for safe and effective Laser Hair Removal Dubai, Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai is the ultimate choice. Led by Celebrity Doctor in Dubai, Dr. Perfect, the clinic offers Laser Hair Removal in Dubai with advanced technology and expert care. Whether you are male or female, patients can enjoy Permanent Hair Removal in Dubai at competitive rates, starting at AED 299 (excluding VAT).
By choosing Perfect Doctors Clinic in Dubai, you’re opting for Best Laser Hair Removal in Dubai, celebrity-level care, and long-lasting smooth skin.






