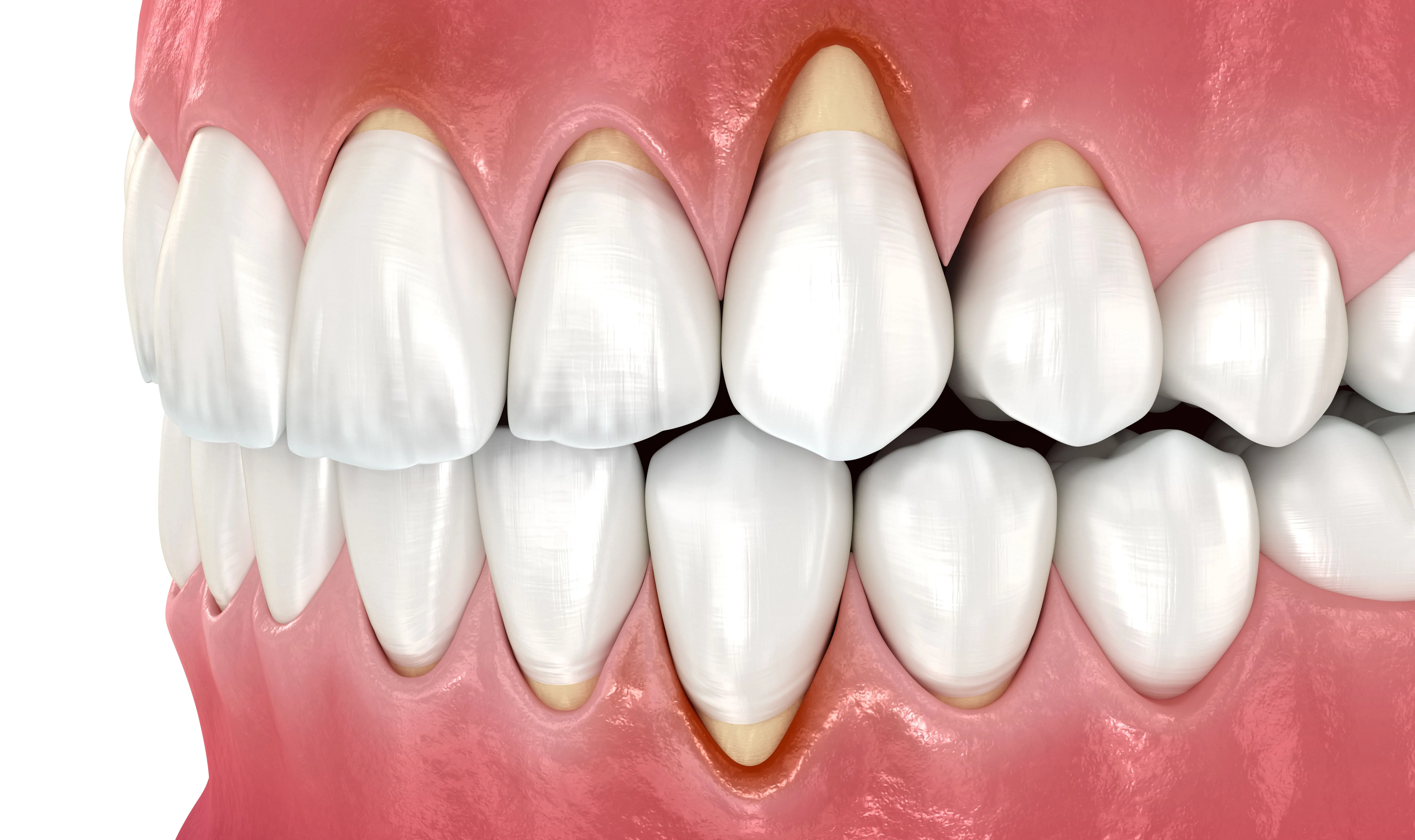
Have you noticed your teeth looking longer or feeling more sensitive lately? It could be a sign of gum recession a condition where gum tissue gradually pulls away from the teeth, exposing the roots beneath. This exposure not only causes sensitivity but can also increase your risk of tooth decay and even tooth loss if left untreated.
Gum recession is more common than many people think, but it’s not a normal part of aging. The good news is that it can be prevented and, in many cases, effectively treated. This article explains what causes gum recession, how to prevent it, and the best treatment options to restore healthy gums and protect your smile.
What Is Gum Recession?
Healthy gums play a vital role in protecting your teeth. They form a tight seal around each tooth, shielding the roots and supporting overall oral health. When gums recede, this protective barrier weakens, exposing the root surfaces. These roots are more sensitive because they lack enamel, making them vulnerable to decay, wear, and discomfort. Although gum recession can affect anyone, it tends to become more noticeable with age. However, aging itself isn’t the cause it’s usually due to factors like improper brushing, gum disease, or lifestyle habits that damage the gum tissue over time.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Gum Recession
Gum recession often develops slowly, which is why early signs are easy to miss. Some of the most common symptoms include: Teeth that appear longer than before, visible root surfaces near the gumline, or increased sensitivity when eating hot, cold, or sweet foods. You may also notice notches near the gumline, red or swollen gums, and bleeding when brushing or flossing. In more advanced cases, teeth can loosen slightly, or your bite may begin to feel different. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see your dentist promptly early treatment can prevent more serious damage.
What Causes Gum Recession?
Aggressive Brushing
Brushing your teeth too hard or using a stiff-bristled toothbrush can wear away delicate gum tissue over time. Proper brushing technique using gentle, circular motions is key to protecting your gums.
Gum Disease (Periodontitis)
One of the most common causes of gum recession is gum disease, a bacterial infection that damages gum tissue and bone. As the gums pull away from the teeth, deep pockets form, leading to further recession and potential tooth loss.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Neglecting daily brushing and flossing allows plaque and tartar to accumulate, irritating the gums and triggering inflammation that causes them to recede.
Tobacco Use
Smoking or chewing tobacco restricts blood flow and slows the healing process, making the gums more prone to infection and shrinkage.
Misaligned Teeth or Bite Problems
When teeth don’t align properly, certain areas of the mouth experience excess pressure during chewing, which can damage gums and supporting bone.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or puberty can make gums more sensitive and reactive to plaque buildup, increasing the risk of recession.
Genetics
Some people naturally have thinner or more delicate gum tissue, making them genetically predisposed to gum recession.
Teeth Grinding or Clenching (Bruxism)
Chronic grinding or clenching places too much force on the teeth and gums, contributing to tissue breakdown and gum recession.
Why Gum Recession Is a Serious Problem
How to Prevent Gum Recession
Brush Gently and Correctly
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush with light, circular motions instead of harsh scrubbing. Proper brushing technique cleans effectively without damaging your gums.
Floss Daily
Flossing helps remove plaque between teeth and along the gumline where your toothbrush can’t reach, reducing the risk of gum inflammation.
Maintain Regular Dental Checkups
Routine dental visits every six months allow your dentist to detect early signs of gum disease and remove hardened tartar before it causes damage.
Quit Smoking or Tobacco Use
Eliminating tobacco products improves gum health, boosts blood flow, and lowers your risk of gum disease.
Use a Mouthguard if You Grind Your Teeth
If you grind your teeth, wearing a custom mouthguard can protect your teeth and gums from excessive pressure during sleep.
Choose the Right Toothpaste and Mouthwash
Select gentle, fluoride-based products designed for sensitive teeth or gum health. Avoid abrasive toothpaste that can wear away gum tissue.
Eat a Balanced Diet
A nutrient-rich diet that includes vitamin C, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids supports strong gums and reduces inflammation.
Treatment Options for Gum Recession
Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing)
This non-surgical treatment removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooths the root surfaces, helping gums reattach to the teeth and heal.
Gum Grafts
In cases of significant recession, a gum graft may be recommended. Tissue from another area of your mouth or a donor source is grafted over the exposed roots, restoring the gumline and protecting the teeth.
Pinhole Surgical Technique
This minimally invasive procedure involves small entry points in the gums to gently reposition existing tissue over exposed areas, with little to no sutures required.
Desensitizing Treatments
Fluoride gels or bonding agents can be applied to exposed roots to reduce sensitivity and strengthen enamel.
Orthodontic Treatment
If gum recession is caused by misaligned teeth or bite issues, orthodontic correction can redistribute pressure and prevent further gum damage.
When to See a Dentist
Recognizing Early Warning Signs
Gum recession often develops gradually, which means you might not notice it until the damage becomes more visible. However, early detection makes a big difference. If you experience persistent tooth sensitivity especially to temperature changes or sweet foods it could signal exposed roots. You may also notice your teeth appearing longer than before, small gaps near the gumline, or even a dark line where the gum has receded. These are clear indicators that you should schedule a dental appointment as soon as possible.
Other Symptoms That Require Attention
In addition to sensitivity or visible gum recession, other concerning signs include red, swollen, or bleeding gums when brushing or flossing. Loose teeth or a shifting bite where your teeth no longer fit together comfortably may indicate that gum disease or bone loss has already begun. Chronic bad breath or a persistent bad taste can also suggest bacterial buildup beneath the gums.
Why Early Treatment Matters
Ignoring early symptoms of gum recession can allow the condition to progress, leading to more serious complications such as bone loss, infection, or tooth loss. Prompt dental evaluation ensures that the cause whether it’s gum disease, aggressive brushing, or teeth grinding is properly identified and treated. Early intervention can often reverse mild gum damage and prevent the need for surgical procedures later on.
What to Expect During a Dental Visit
During your appointment, the dentist will perform a thorough gum examination, measure pocket depths around your teeth, and may take digital X-rays to assess bone health. If gum disease is detected, treatments such as deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) may be recommended. For more advanced cases, your dentist might discuss surgical options like gum grafting or the pinhole technique to restore gum coverage and protect your tooth roots.
Protecting Your Smile Moving Forward
After treatment, your dentist will provide guidance on proper brushing techniques, recommended oral care products, and lifestyle adjustments to prevent future gum recession. Regular checkups every six months allow your dentist to monitor your gum health and ensure early correction of any recurring issues.
How to Keep Gums Healthy Long-Term
Stay Hydrated for Better Oral Health
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps wash away bacteria and food debris while promoting saliva production. Saliva is essential for neutralizing acids and keeping your gums moist and healthy.
Avoid Harmful Habits
Tobacco use is one of the biggest threats to gum health. Smoking or chewing tobacco reduces blood flow to the gums and slows healing. Likewise, avoid clenching or grinding your teeth, as excessive pressure can damage the tissues that support your gums.
Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Regular dental checkups every six months are crucial for long-term gum care. Professional cleanings remove tartar buildup that daily brushing and flossing can’t eliminate. Your dentist can also identify early signs of gum disease or recession and provide preventive treatments before they worsen.
Manage Stress to Protect Your Gums
Chronic stress can contribute to teeth grinding (bruxism) and inflammation, both of which harm your gums. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing, exercise, or meditation to protect your oral and overall health.
Support Gum Health Through Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in vitamins C and D, calcium, and antioxidants helps strengthen your gums and immune response. Fresh fruits, leafy greens, and dairy products can promote healing and maintain strong gum tissue.
Conclusion: Protecting the Foundation of Your Smile
Gum recession may progress slowly, but it is a clear warning sign that your gums and supporting bone need attention. Left untreated, it can lead to root decay, tooth sensitivity, and eventually tooth loss all of which can impact your ability to eat, speak, and smile confidently. However, the encouraging truth is that gum recession is both treatable and preventable with the right approach.
Consistent oral hygiene, gentle brushing, and professional dental cleanings play a vital role in keeping your gums strong and healthy. Regular dental visits allow your dentist to detect early signs of gum disease or tissue loss before they worsen, ensuring that you receive timely and effective care. Modern treatments such as scaling and root planing, gum grafts, and the pinhole surgical technique can restore gum coverage, protect tooth roots, and enhance your smile’s appearance.






