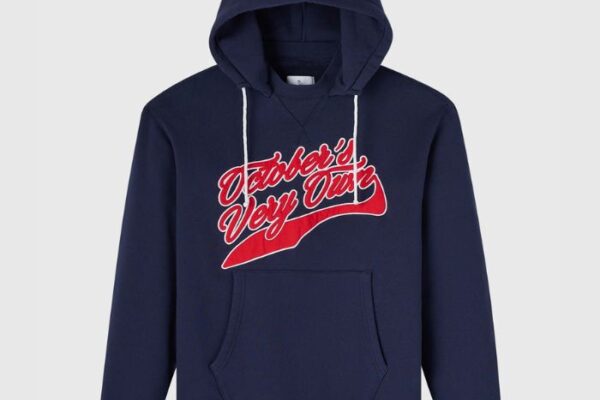
As sustainability becomes a defining factor in modern fashion, consumers are increasingly seeking clothing that aligns with their values without compromising comfort or style. The eco-friendly essentials hoodie represents this shift—a thoughtfully designed Essential Hoodie garment that combines everyday wearability with responsible production. More than just a casual staple, it reflects a commitment to environmental awareness, ethical sourcing, and long-lasting quality.This explores what makes an eco-friendly essentials hoodie special, why it matters in today’s fashion landscape, and how it seamlessly fits into a modern, conscious wardrobe.
The Growing Demand for Sustainable Fashion
The fashion industry has long been associated with environmental impact, from excessive water usage to textile waste and carbon emissions. As awareness grows, consumers are rethinking their choices, favoring durable, ethically made garments over fast fashion.
An eco-friendly essentials hoodie answers this demand by focusing on sustainability at every stage—from material selection to manufacturing and long-term wear. It proves that everyday fashion can be both stylish and responsible.
What Makes a Hoodie Eco-Friendly?
An eco-friendly essentials hoodie is defined by thoughtful design and sustainable practices.
Sustainable Materials
Many eco-friendly hoodies are made using organic cotton, recycled polyester, or innovative fabric blends that reduce environmental impact. Organic cotton is grown without harmful pesticides, conserving water and protecting ecosystems.
Responsible Manufacturing
Ethical production methods prioritize fair wages, safe working conditions, and reduced waste. Some brands also use renewable energy and water-saving processes during manufacturing.
Low-Impact Dyes
Eco-conscious hoodies often use low-impact or natural dyes, minimizing chemical runoff and water pollution.
Comfort Without Compromise
Sustainability doesn’t mean sacrificing comfort. Eco-friendly essentials hoodies are designed for everyday wear.
Soft, Natural Feel
Organic and recycled materials offer a soft texture that feels gentle against the skin, making the hoodie ideal for all-day use.
Breathable Fabric
Natural fibers promote airflow and temperature regulation, ensuring comfort across seasons.
Durable Construction
Sustainable hoodies are often built to last, reducing the need for frequent replacements and supporting long-term wear.
Timeless Design for Long-Term Use
One of the core principles of sustainable fashion is longevity. Eco-friendly essentials hoodies embrace timeless design to remain relevant beyond seasonal trends.
Minimalist Aesthetic
Clean lines, subtle details, and neutral tones ensure the hoodie pairs effortlessly with a wide range of outfits.
Versatile Fit
Whether classic or relaxed, the fit is designed to suit various body types and styling preferences.
Everyday Functionality
From lounging and commuting to casual outings, the hoodie adapts to diverse lifestyles.
Styling the Eco-Friendly Essentials Hoodie
Sustainable fashion doesn’t limit creativity. An eco-friendly hoodie offers plenty of styling options.
Casual Comfort
Pair it with jeans or joggers for a relaxed, everyday look that feels intentional and modern.
Layered Outfits
Use the hoodie as a mid-layer under jackets or over base layers for added warmth and dimension.
Smart-Casual Approach
Combine a neutral eco-friendly hoodie with tailored trousers and clean footwear for a refined yet comfortable outfit.
Seasonal Versatility
Eco-friendly essentials hoodies are designed to work year-round.
-
Fall: Perfect for cool mornings and evenings
-
Winter: Ideal as a warm mid-layer
-
Spring: Lightweight enough for transitional weather
-
Summer Nights: Comfortable for breezy or air-conditioned spaces
This adaptability increases their value and reduces the need for multiple seasonal garments.
Environmental Benefits of Choosing Eco-Friendly Hoodies
Opting for an eco-friendly essentials hoodie contributes to positive environmental change.
Reduced Resource Consumption
Sustainable materials require less water and energy than conventional fabrics.
Lower Carbon Footprint
Ethical manufacturing practices and recycled materials help minimize emissions.
Less Waste
Durable construction and timeless design reduce garment turnover and landfill waste.
Every eco-friendly purchase supports a shift toward more responsible fashion consumption.
Sustainability Meets Durability
Durability is a key aspect of sustainability. A well-made eco-friendly hoodie maintains its shape, color, and comfort over time, even with frequent wear.
Reinforced seams, quality stitching, and resilient fabrics ensure longevity, making the hoodie a reliable wardrobe staple rather than a disposable item.
Who Should Choose an Eco-Friendly Essentials Hoodie?
An eco-friendly essentials hoodie is ideal for:
-
Environmentally conscious consumers
-
Minimalists building a capsule wardrobe
-
Professionals seeking refined casualwear
-
Students and creatives who value ethical fashion
-
Anyone wanting to make more responsible clothing choices
Its universal appeal makes it suitable for a wide range of lifestyles.
Caring for Your Eco-Friendly Hoodie
Proper care further enhances sustainability.
-
Wash in cold water to save energy
-
Use eco-friendly detergents
-
Air dry or tumble dry on low heat
-
Avoid over-washing
These habits extend the hoodie’s lifespan and reduce environmental impact.
Why Eco-Friendly Essentials Hoodies Are the Future
As sustainability becomes central to Essentials Sweatpants fashion, eco-friendly essentials hoodies represent a future where quality, comfort, and responsibility coexist. They encourage mindful consumption and demonstrate that everyday clothing can be produced with care for both people and the planet.By choosing eco-friendly options, consumers help drive industry-wide change toward more ethical and sustainable practices.
Final Thoughts
The eco-friendly essentials hoodie is more than just a wardrobe staple—it’s a statement of values. Combining sustainable materials, ethical production, timeless design, and everyday comfort, it reflects a modern approach to fashion that prioritizes responsibility without sacrificing style.In a world increasingly focused on conscious living, investing in an eco-friendly essentials hoodie means choosing durability, versatility, and environmental care. It’s a small but meaningful step toward a more sustainable future—one comfortable hoodie at a time.